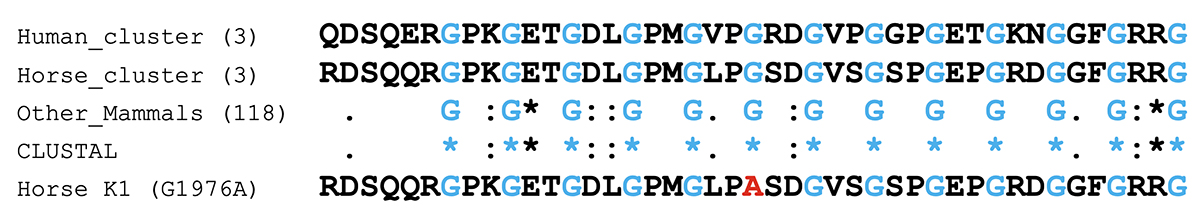Blog
K1 Allele of COL6A3

Introduction
This blog post explores the K1 allele of the equine COL6A3 gene, which encodes Collagen type VI alpha 3 chain. Portions of this blog post serve as additional sources of information to supplement the COL6A3 Gene Page.
The K1 allele of COL6A3 carries a missense mutation, shown below. The protein model XP_014595871.3 was used to assign amino acid positions.
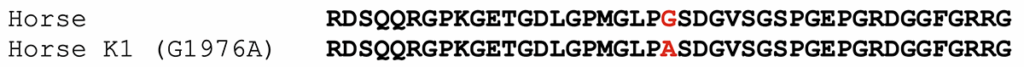
Figure 1. Alignment of partial COL6A3 protein sequences from horse, compared to the K1 variant. The position of the amino acid affected by the substitution is highlighted in red.
We present data to support the hypothesis that the K1 allele of COL6A3 is damaging.
The K1 variant (G1976A) substitutes an alanine for a glycine. The affected amino acid is in the triple-helical portion of COL6A3. The general sequence of this region in all collagens is GLY-X-Y, where every third amino acid is a glycine. The X and Y amino acids are generally poorly conserved. In the formation of the collagen triple-helical region, the glycine residues are points of contact between helices. Glycine has the smallest R group of any amino acid (a hydrogen atom). Other amino acids in these positions interfere with triple helix formation to some extent. For further discussion, please the blog post on the K1 variant of COL6A3.
Comparing COL6A3 protein sequences from multiple species
Evolutionary conservation provides evidence on whether the K1 allele of COL6A3 is damaging. In this approach, predicted COL6A3 protein sequences are compared among a number of different species. Amino acid substitutions that have gone to fixation in one or more species are assumed to be selectively neutral; mutations in conserved residues that have not gone to fixation in any species are likely damaging.
The 43-amino-acid portion of COL6A3 centered on the K1 variant, shown above, was used to conduct blastp searches of the protein sequence database at NCBI, retrieving sequences from mammals. Sequences from multiple species in the mammalian lineage were used to conduct blastp searches. See the Technical Appendix for details.
Evolutionary Conservation of K1: Mammals
The sequence of the 43-amino acid portion of COL6A3 centered on the K1 variant is poorly conserved among mammals, with the exception of the glycine residues, as expected. After clustering of identical sequences, there are 66 unique sequences among 124 mammals. Results are shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Alignment of partial COL6A3 protein sequences from mammals, centered on the position of the K1 variant (highlighted in red). Several partial mammalian COL6A3 sequences centered on the K1 variant were used as blastp queries to retrieve COL6A3 protein sequences from mammals. Sequences that were identical were clustered. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of species in a cluster. CLUSTAL output summarizes whether a particular position is a single and fully conserved residue (*), has a conservative substitution with strongly similar properties (:), a somewhat conservative substitution (.), or is not conserved ( ). The sequence of the horse K1 allele G1967A is shown for comparison, but was not included in the CLUSTAL analysis. See the Technical Appendix for details.
The G1976 allele (highlighted in red) is fully conserved in 124 species of mammals. The G1976A allele is only seen as a minor allele in horse.
The multiple alignment shown in Figure 2 highlights the GLY-X-Y sequence of the triple helical region, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Alignment of partial COL6A3 protein sequences from mammals, centered on the position of the K1 variant (highlighted in red). The data shown in Figure 2 are presented with sequences from most mammals compressed into a single line showing 118 other mammals; human and horse sequences are shown separately. The fully conserved glycine residues in the triple helical region are highlighted in blue. CLUSTAL output summarizes whether a particular position is a single and fully conserved residue (*), has a conservative substitution with strongly similar properties (:), a somewhat conservative substitution (.), or is not conserved ( ). The sequence of the horse K1 allele G1967A is shown for comparison, but was not included in the CLUSTAL analysis. See the Technical Appendix for details.
Summary
The conservation of glycine residues in the triple helical region of collagen proteins, including COL6A3, is a general feature of this family of proteins, as illustrated in this post.
We identified 124 mammalian COL6A3 sequences using a 43-amino acid frame of equine COL6A3 that includes the equine K1 variant (COL6A3-G1976A). These sequences cluster into 66 unique sequences. The 43-amino acid frame includes 13 glycine residues in the triple helical region (GLY-X-Y). All 13 glycine residues are fully conserved across all 66 unique sequences representing 124 mammals.
The results support the hypothesis that the K1 variant of equine COL6A3 is damaging.
Technical Appendix
The purpose of this technical appendix is to permit researchers to reproduce these results independently.
The equine K1 allele is a missense allele that causes an amino acid substitution. At the DNA level, the allele is described as the coordinates and base change in EquCab3.0:
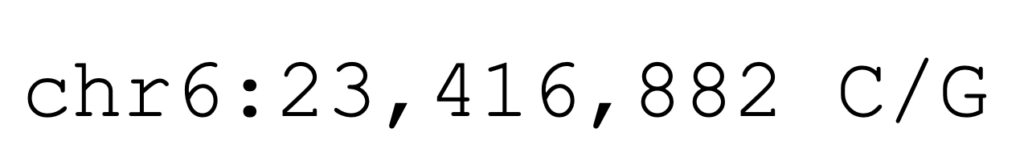
Using the amino acid positions from the protein model XP_014595871.3 allows the missense allele to be described as COL6A3-G1976A, shown below.
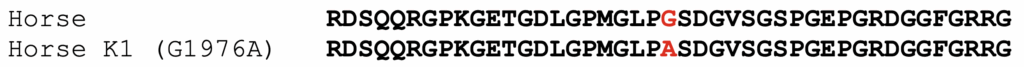
Click the link to the UCSC Genome Browser to view the horse genome sequence centered on the position of the COL6A3-G1967A (K1) allele.
Retrieving protein sequences. Protein sequences like those shown in the alignments (Figures 2, 3) can be retrieved from NCBI using the blastp tool and a query sequence.
There are multiple genes encoding various collagens. The query sequences used for this analysis have segments of collagen triple helix, a low-complexity sequence with the general sequence GLY-X-Y. The 43-amino acid query sequences used here have six amino acids outside the triple helical region, which makes it possible to retrieve COL6A3 sequences as opposed to sequences from other collagens.
In some species, the genome assembly in the region covered by the query sequence is incomplete. Such cases can be recognized by alignment to the triple helical region but not to the entire query sequence. These sequences were excluded from further analysis.
Go to the BLASTp server at NCBI.
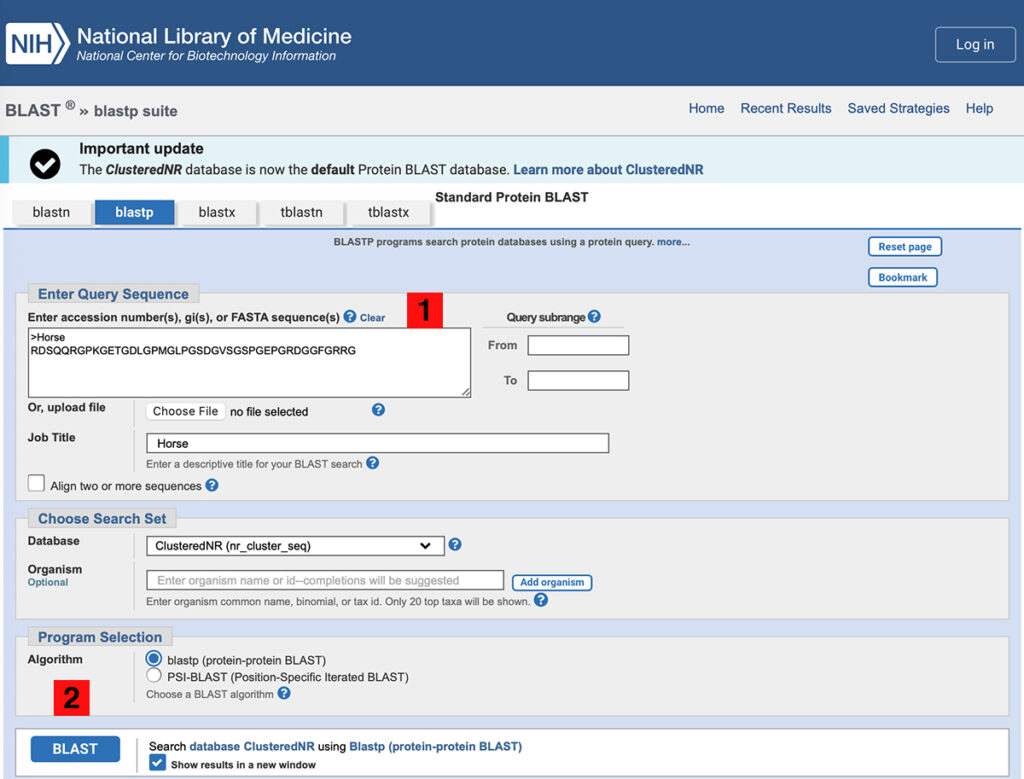
1. For the query sequence, use:
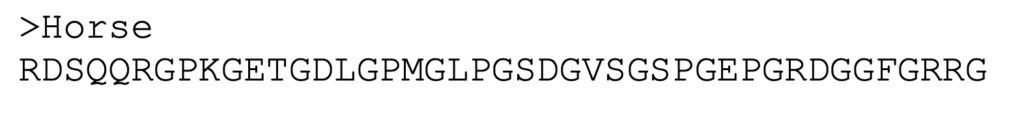
2. Click “BLAST”
Results are returned as alignments. Here are the results for Brown rat vs the horse query.
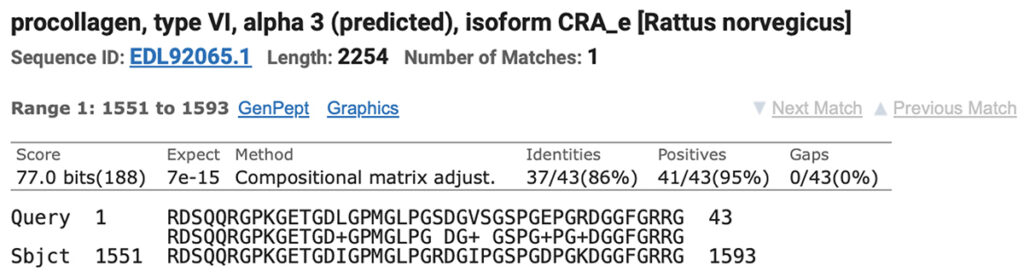
3. The sequence can be copied from this result, and used for an additional search.
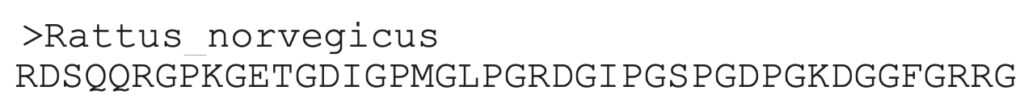
Aligning protein sequences
Multiple protein sequences were aligned using CLUSTAL.
Evolutionary relationships
Information on evolutionary relationships among species is presented graphically as the Tree of Life.
Download data
The data used for alignments in Figure 3 are available as a downloadable spreadsheet.
The spreadsheet contains the species name, common name, sequence ID, partial sequence, and cluster for each species.
Share this post
From the blog
The latest industry news, interviews, technologies, and resources.
A Drug for PSSM?
INTRODUCTION A new drug that inhibits glycogen synthase I, encoded by GYS1, reduces…
EquiSeq Featured in Albuquerque Journal
ALBUQUERQUE, NEW MEXICO – January 11, 2026 EquiSeq was profiled in the Business…